Invoking Open Match APIs
Open Match has a resource-based REST API that is served from HTTP and gRPC. It also complies with the OpenAPI (fka Swagger) API specification which means it’s easy to download the schema and generate clients in many different languages.
Open Match default hostnames and endpoints
The following defines the in-cluster hostnames and endpoints of Open Match’s external services. The corresponding Helm configurations used to generate these configs could be found here.
swaggerui:
hostName: om-swaggerui
httpPort: 51500
query:
hostName: om-query
grpcPort: 50503
httpPort: 51503
frontend:
hostName: om-frontend
grpcPort: 50504
httpPort: 51504
backend:
hostName: om-backend
grpcPort: 50505
httpPort: 51505
Invoking Open Match gRPC APIs
We recommend using gRPC to talk to Open Match.
The following is an example of an in-cluster program that creates a vanilla gRPC client to talk to Open Match Frontend and then calls frontend.CreateTicket method.
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"open-match.dev/open-match/pkg/pb"
"open-match.dev/open-match/pkg/structs"
)
func main() {
// Create a gRPC frontend client
conn, err := grpc.Dial("om-frontend:50504"), grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("grpc.Dial failed with %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
feClient := pb.NewFrontendClient(conn)
// Create an Open Match CreateTicketRequest with Open Match's public package
sent := &pb.CreateTicketRequest{
Ticket: &pb.Ticket{
SearchFields: &pb.SearchFields{
Tags: []string{"beta-gameplay"},
},
},
}
ticket, err := feClient.CreateTicket(sent)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("feClient.CreateTicket failed with %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("Open Match assigned id %s to the ticket", ticket.GetId())
}
Invoking Open Match HTTP APIs
Open Match provides REST API for all of its external components using the grpc-gateway plugin. Below is a vanilla in-cluster Go program to interact with Open Match via its HTTP endpoint. Please see the Open Match’s API definitions for the latest HTTP endpoints each service is using.
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
"github.com/golang/protobuf/jsonpb"
"open-match.dev/open-match/pkg/pb"
"open-match.dev/open-match/pkg/structs"
)
func main() {
var m jsonpb.Marshaler
// The HTTP endpoint of frontend.CreateTicket API
apiURL := fmt.Sprintf("http://om-frontend:%d/v1/frontendservice/tickets", 51504)
// Create an Open Match CreateTicketRequest with Open Match's public package
sent := &pb.CreateTicketRequest{
Ticket: &pb.Ticket{
SearchFields: &pb.SearchFields{
Tags: []string{"beta-gameplay"},
},
},
}
payload, err := m.MarshalToString(&sent)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("m.MarshalToString(%#v) failed with %v; want success", payload, err)
}
// Send the Request to frontend.CreateTicket endpoint
resp, err := http.Post(apiURL, "application/json", strings.NewReader(payload))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("http.Post(%q) failed with %v, want success", apiURL, err)
}
defer resp.Close()
buf, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body) failed with %v; want success", err)
}
// Unmarshal the response to a Go struct
var received *pb.Ticket
if err := jsonpb.UnmarshalString(string(buf), received); err != nil {
log.Errorf("jsonpb.UnmarshalString(%s, &msg) failed with %v; want success", buf, err)
}
fmt.Println("Open Match assigned id %s to the ticket", received.GetId())
}
Invoking Open Match APIs via the Swagger UI
You can view and talk to this API via the Swagger UI application that is deployed with your Open Match cluster.
Google Kubernetes Engine
If your cluster runs on GKE you can access the tool from your cluster using a Public IP address.
Go to Cloud Console > Kubernetes Engine > Services & Ingress and look for om-swaggerui.
In that row, there’s a link to view the API browser.
Locally
The Swagger UI is accessible from your cluster via port 51500. Kubernetes’s virtual network is by default private so you’ll need to add a proxy to communicate with it.
# Open the port to the pod so that it can be accessed locally.
kubectl port-forward --namespace open-match service/om-swaggerui 51500:51500
From there you can access the proxy from http://localhost:51500.
Using the Swagger UI
Swagger UI is a generic tool for viewing APIs and interacting with them.
Open Match has many APIs but the default one is the Frontend.
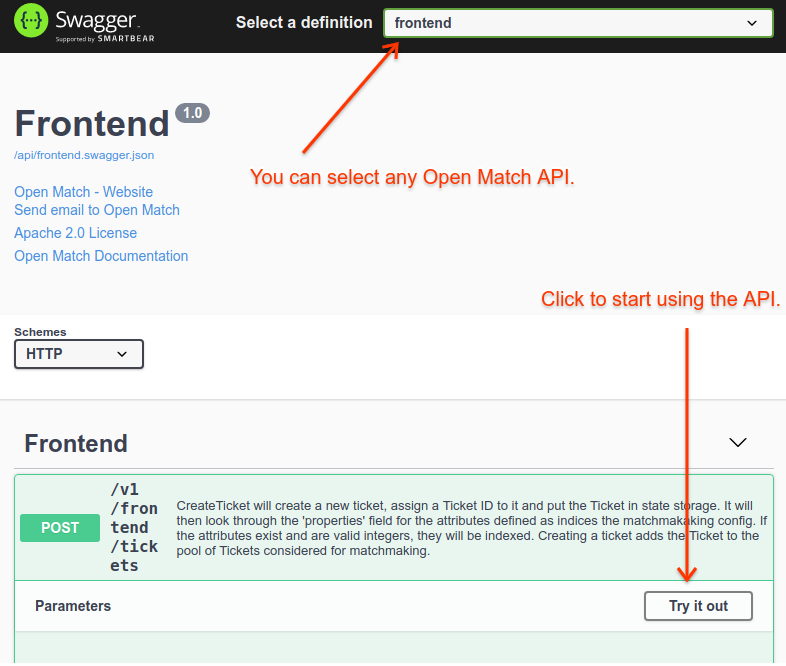
By clicking on a function you can see the schema of the API. To call an API click
Try it out and then fill in body and then select Execute. You’ll then see the
HTTP code and response.
Disable Swagger UI
For security purposes you will want to disable the Swagger UI application by setting
--set open-match-core.swaggerui.enabled=false in the helm command or add the following
YAML to your values.yaml.
open-match-core:
swaggerui:
enabled: false
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.
Last modified June 17, 2025